Human detecting Robot, PROJECT
Human
detecting ROBOT for Earth quake rescue operation
Details
description
1.1 INTRODUCTION
The advent of new
high-speed technology and the growing computer capacity provided realistic
opportunity for new robot controls and realization of new methods of control
theory.
This technical improvement together with the
need for high performance robots created faster, more accurate and more
intelligent robots using new robots control devices,
new drives and advanced control algorithms.
This Project deals
with live personal detection, robot is based on 8 bit Microcontroller. This
Robot follows which is drawn over the surface.
Here we are using PIR sensor for detecting the
human. The project is mainly used in the DEBRIS for Earth quake rescue.
Internally it
consists of IR sensors. The infrared sensors are used to sense the live
persons. All the above systems are controlled by the Microcontroller.
In our project we are
using the popular 8 bit microcontroller.
The Microcontroller
is used to control the motors. It gets the signals from the PIR sensors and it
drives the motors according to the sensor inputs.
Two DC Gare motors are used to drive the
robot.
HARDWARE
REQUIREMENTS
1. POWER SUPPLY
2. MICRO CONTRODLLER (AT89S52)
3. DC GARE MOTOR
4. RELAYS
5.PIR SENSOR
SIMULATION
TOOL: KEIL MICROVISION
LANGUAGE: EMBEDDED “C “LANGUAGE
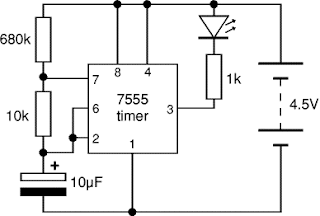
1.2BLOCK DIAGRAM :
1.3 Flow chart and Algorithm
ALGORITHM
Step 1:
Start
Step 2:
Initialize micro controller
Step 3:
Initialize motors
Step 4:
Initialize PIR sensor
Step 5:
Monitor PIR sensor
Step 6: If
person detected
Buzzer on
motor
rotates in specified direction
Step 7:
Monitor PIR sensor
Step 8:
Stop
CHAPTER 2
DESCRIPTION
OF HARDWARE COMPONENTS
2.1 AT89S52
2.1.1 A
BRIEF HISTORY OF 8051
In 1981,
Intel corporation introduced an 8 bit microcontroller called 8051. this
microcontroller had 128 bytes of RAM, 4K bytes of chip ROM,
two timers, one serial port, and four ports
all on a single chip. At the time it was also referred as “ A SYSTEM ON A CHIP”
The 8051 is
an 8-bit processor meaning that the CPU can work only on 8 bits data at a time.
Data larger than 8 bits has to be broken into 8 bits pieces to be processed by
the CPU.
The 8051 has a total of four I\O ports each 8
bit wide.
There are
many versions of 8051 with different speeds and amount of on-chip ROM and they
are all compatible with the original 8051.
this means that if you write a program for one
it will run on any of them.
The 8051 is
an original member of the 8051 family. There are two other
members in
the 8051 family of microcontrollers. They are 8052 and 8031. All the three
microcontrollers
will have the same internal architecture, but they differ in the following
aspects.
• 8031 has
128 bytes of RAM, two timers and 6 interrupts.
• 8051 has
4K ROM, 128 bytes of RAM, two timers and 6 interrupts.
• 8052 has
8K ROM, 256 bytes of RAM, three timers and 8 interrupts.
Of the
three microcontrollers, 8051 is the most preferable. Microcontroller supports
both serial and parallel communication.
In the
concerned project 8052 microcontroller is used. Here microcontroller used is
AT89S52, which is manufactured by ATMEL laboratories.
NECESSITY
OF MICROCONTROLLERS:
Microprocessors
brought the concept of programmable devices and made many applications of
intelligent equipment.
Most applications, which do not need large
amount of data and program memory, tended to be costly.
The
microprocessor system had to satisfy the data and program requirements so,
sufficient RAM and ROM are used to satisfy most applications
.The
peripheral control equipment also had to be satisfied. Therefore, almost
all-peripheral chips were used in the design.
Because of these additional peripherals cost
will be comparatively high.
An example:
8085 chip
needs:
An Address
latch for separating address from multiplex address and data.32-KB RAM and
32-KB ROM to be able to satisfy most applications.
As also
Timer / Counter, Parallel programmable port, Serial port, and Interrupt
controller are needed for its efficient applications.
In
comparison a typical Micro controller 8051 chip has all that the 8051 board has
except a reduced memory as follows.
4K bytes of
ROM as compared to 32-KB, 128 Bytes of RAM as compared to 32-KB.
Bulky:
On
comparing a board full of chips (Microprocessors) with one chip with all
components in it (Microcontroller).
Debugging:
Lots of
Microprocessor circuitry and program to debug. In Micro controller there is no
Microprocessor circuitry to debug.
Slower
Development time: As we have observed Microprocessors need a lot of debugging
at board level and at program level, where as, Micro controller do not have
the excessive circuitry and the built-in
peripheral chips are easier to program for operation.
So
peripheral devices like Timer/Counter, Parallel programmable port, Serial
Communication Port, Interrupt controller and so on,
which were most often used were integrated
with the Microprocessor to present the Micro controller .RAM and ROM also were
integrated in the same chip.
The ROM size was anything from 256 bytes to
32Kb or more. RAM was optimized to minimum of 64 bytes to 256 bytes or more.
Microprocessor has following instructions to
perform:
1. Reading
instructions or data from program memory ROM.
2.
Interpreting the instruction and executing it.
3.
Microprocessor Program is a collection of instructions stored in a Nonvolatile
memory.
4. Read
Data from I/O device
5. Process
the input read, as per the instructions read in program memory.
6. Read or
write data to Data memory.
7. Write
data to I/O device and output the result of processing to O/P device.
2.1.2
Introduction to AT89S52
The system
requirements and control specifications clearly rule out the use of 16, 32 or
64 bit micro controllers or microprocessors.
Systems using these may be earlier to
implement due to large number of internal features.
They are also faster and more reliable but,
the above application is satisfactorily served by 8-bit micro controller.
Using an inexpensive 8-bit Microcontroller
will doom the 32-bit product failure in any competitive market place.
Coming to
the question of why to use 89S52 of all the 8-bit Microcontroller available in
the market the main answer would be because
it has 8kB
Flash and 256 bytes of data RAM32 I/O lines, three 16-bit timer/counters, a
Eight-vector two-level interrupt architecture,
a full
duplex serial port, on-chip oscillator, and clock circuitry.
In
addition, the AT89S52 is designed with static logic for operation down to zero
frequency and supports two software selectable power saving modes.
The Idle Mode stops the CPU while allowing the
RAM, timer/counters, serial port, and interrupt system to continue functioning.
The Power
Down Mode saves the RAM contents but freezes the oscillator, disabling all
other chip functions until the next hardware reset.
The Flash program memory supports both
parallel programming and in Serial In-System Programming (ISP).
The 89S52 is also In-Application Programmable
(IAP), allowing the Flash program memory to be reconfigured even while the
application is running.
By
combining a versatile 8-bit CPU with Flash on a monolithic chip, the Atmel
AT89S52 is a powerful microcomputer which provides a highly flexible and
cost effective
solution to many embedded control applications.
2.1.3 FEATURES
Compatible
with MCS-51® Products
• 8K Bytes
of In-System Programmable (ISP) Flash Memory
–
Endurance: 1000 Write/Erase Cycles
• 4.0V to
5.5V Operating Range
• Fully
Static Operation: 0 Hz to 33 MHz
•
Three-level Program Memory Lock
• 256 x
8-bit Internal RAM
• 32
Programmable I/O Lines
• Three
16-bit Timer/Counters
• Eight
Interrupt Sources
• Full
Duplex UART Serial Channel
• Low-power
Idle and Power-down Modes
• Interrupt
Recovery from Power-down Mode
• Watchdog
Timer
• Dual Data
Pointer
-Power-off
Flag
(Via a blog... If there are any
mistakes, admin would not be responsible for that.)